BROWSE COURSE CATALOG
Courses and Pathways in Science
Il corso tratta i modelli di stato con un ingresso e un’uscita mettendone in evidenza l’importanza e le principali proprietà. Si mostra anche come costruire tali modelli a partire dalle equazioni della fisica. Gli argomenti trattati nel corso sono: definizioni di modelli di stato, sistemi lineari, costruzione di un modello di stato, scelta delle variabili di stato, punti di equilibrio e linearizzazione, feedback linearization. Analisi dei sistemi lineari: evoluzione dello stato e dell'uscita di un sistema lineare, Teorema di sovrapposizione degli effetti, evoluzione libera ed evoluzione forzata dello stato e dell'uscita, funzione di trasferimento e risposta impulsiva. Stabilità: stabilità nei sistemi lineari, condizioni di stabilità per i punti di equilibrio di sistemi non lineari, stabilità BIBO. Esempi: modelli compartimentali, modello preda-predatore (Lotka-Volterra), modello del motore elettrico.
La conoscenza di base della chimica e della biologia è fondamentale per l'accesso alle lauree triennali in psicologia per comprendere gli approcci metodologici utilizzati in psicologia per studiare il comportamento e la cognizione umana.
L'obiettivo del corso è quello di fornire agli studenti i concetti di base della chimica e della biologia.
Il corso si rivolge a tutti coloro che vogliono recuperare le conoscenze di biologia e chimica per conseguire gli OFA (Obblighi Formativi Aggiuntivi), agli studenti del primo anno dei Corsi di Laurea di Psicologia e a tutti coloro che, mossi dalla curiosità, vogliono conoscere il funzionamento del nostro organismo.
This course will provide a deeper insight about the application of Climate Smart Agriculture and will present advanced understanding of useful practices and techniques that can improve land management in view of biodiversity principles and climate change adaptation needs.

- Instructor: FEDERICA D'ACUNTO
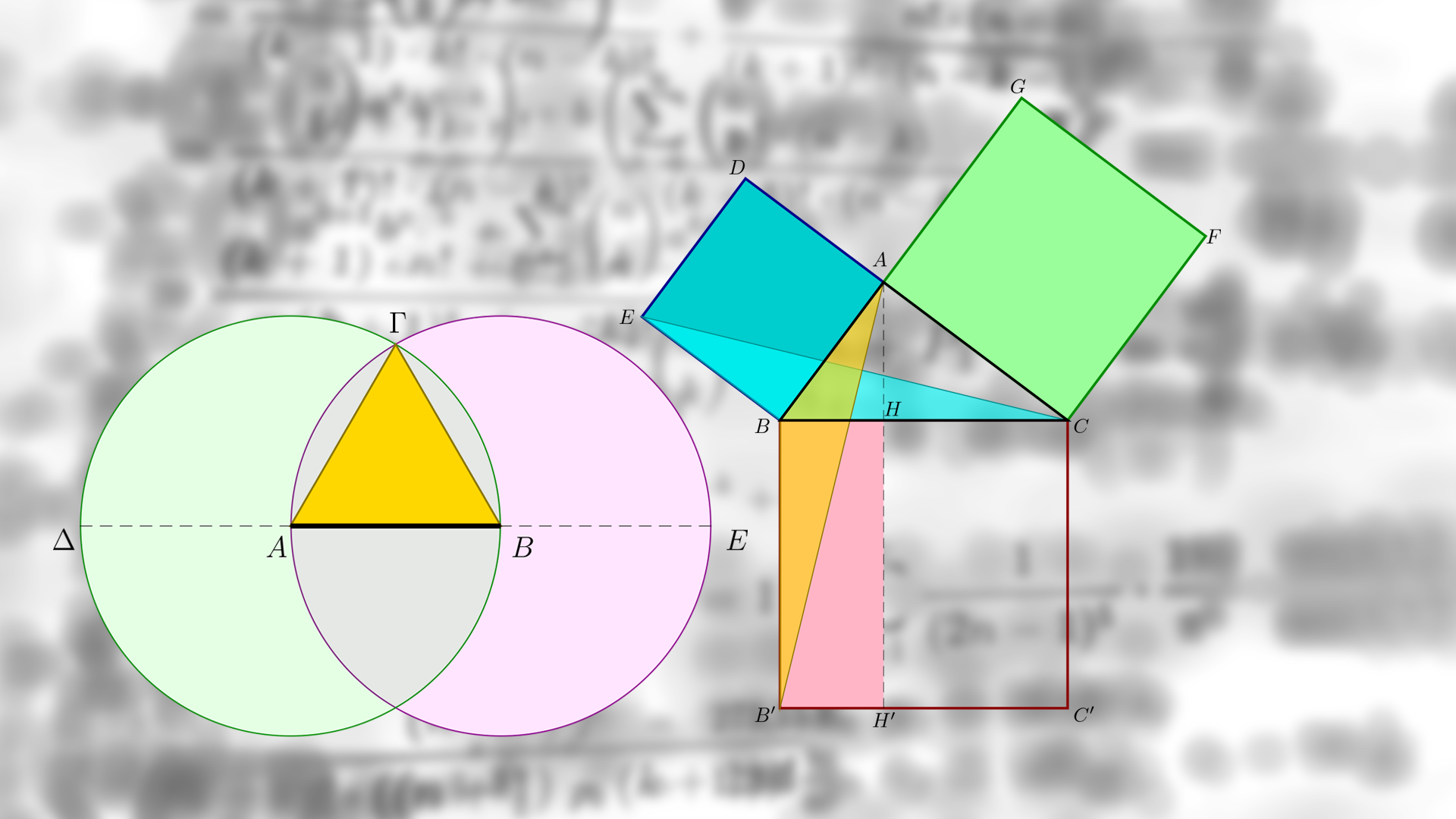
To begin with, the basic notions of set theory and equalities/inequalities properties will be reviewed; after that, the founding postulates will be given, along with first results on straight lines, segments, planes, angles and orthogonality.
In another section, polygons will be introduced and described, with a particular attention to triangles; congruence criteria and basic inequalities are then analysed.
After that, a further section on parallelism issues will introduce rhomboids and basic proportionality Thales’ theorem. Circles and regular polygons will be introduced in another section, along with main results related to those figures.
All results obtained will lead to the final two sections: the first one concerning areas, equivalence, and Euclidean and Pythagorean theorems on right-angled triangles; and the second one dealing with similarity and homothety.
- Instructor: FULVIO BISI
- Instructor: FRANCESCA BATTAGLIA
- Instructor: BELINDA DEL GAUDIO
- Instructor: DANIELE LEONE
- Instructor: CLAUDIO PORZIO
- Instructor: DANIELE PREVITALI
- Instructor: DARIO SALERNO
- Instructor: GABRIELE SAMPAGNARO
- Instructor: MARIAGRAZIA STARITA
- Instructor: GIANPAOLO STELLA
- Instructor: VINCENZO VERDOLIVA
This course will provide key information about what Climate Smart Agriculture is and will present basic understanding of useful practices and techniques that can improve land management in view of biodiversity principles and climate change adaptation needs.
At the end of the course, you will have the possibility to enroll for the Advanced level and test our Online Simulator, a virtual environment where you will have the chance to simulate the benefits on a given area of the implementation of Climate Smart Agriculture measures presented in the MOOC.

This course presents the basic mathematics topics, which are necessary in order to fruitfully follow the Mathematics and Mathematical Analysis courses which are common to all scientific Bachelor courses (e.g., Mathematics, Physics, Engineering, Biological Sciences, Biotechnologies, …).
First, the basic algebraic operations on polynomials and the first notions of analytic geometry in the
plane are reviewed, including, among other things,
the equations of lines, parabolas, circumferences, ellipses, and hyperbolas.
The
concept
of function in the abstract is then introduced and the fundamental functions that are used in Mathematical Analysis are
presented: in addition to polynomial functions, trigonometric, exponential and
logarithmic functions are defined and illustrated.
Finally, the methodologies that allow solving equations and
inequalities, both single and in systems, involving
all the functions covered in the course are addressed.

- Instructor: CLAUDIO DAPPIAGGI
- Instructor: ELISABETTA ROCCA
- Instructor: MARCO VENERONI




